In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a process whereby the eggs are fertilized by a sperm outside of the body, i.e. in laboratory conditions.
In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a process whereby the eggs are fertilized by a sperm outside of the body, i.e. in laboratory conditions. The fertilized egg (embryo) develops and is transferred to the uterus a few days later.
IVF is performed so the couple can overcome fertility problems, such as:
- Blocked fallopian tubes
- Male factor infertility
- Ovarian factor infertility
- Previous unsuccessful insemination attempts
- Unexplained infertility
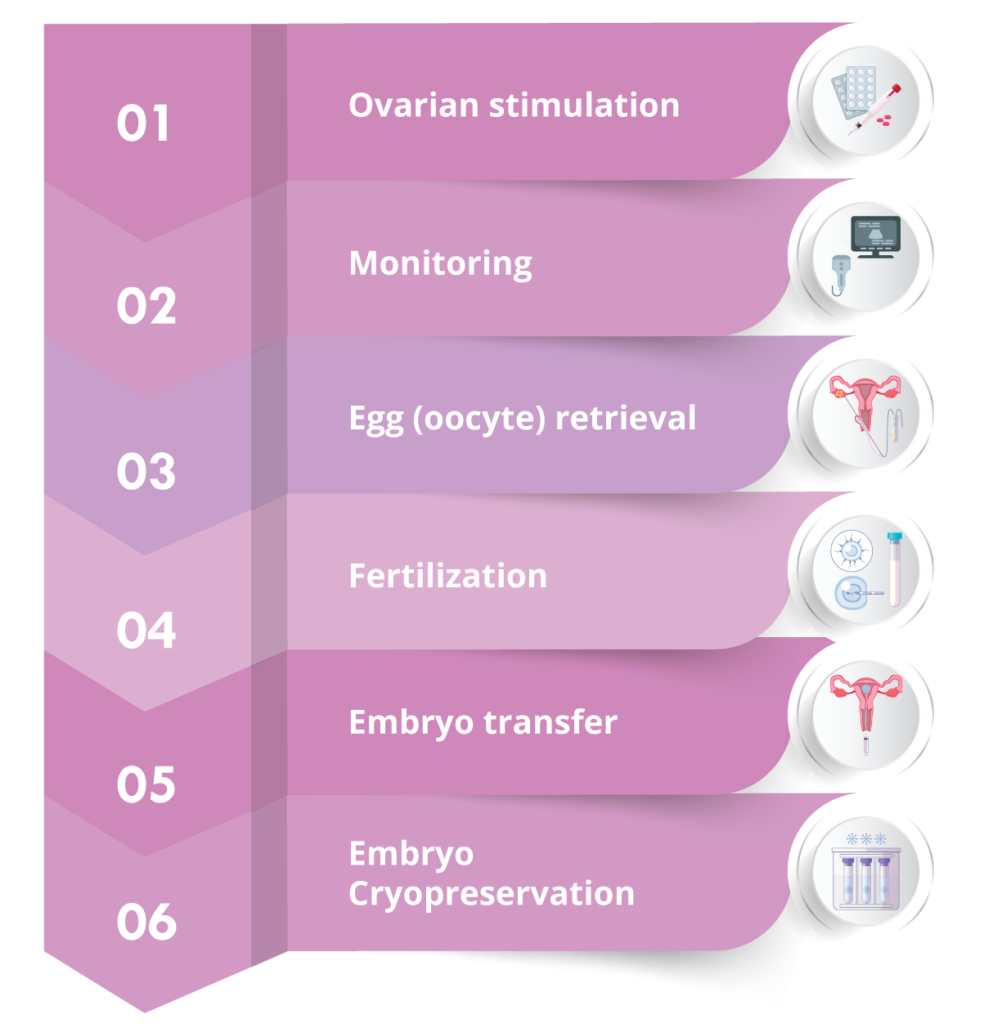
IVF process / stages
The ovaries are stimulated so that more than one egg may be produced. This is achieved with administration of pharmaceutical treatment, either mild (pills) or more effective (gonadotropins). Gonadotropins are administered by subcutaneous injection, usually for about 10-12 days.
Before stimulation begins, an ultrasound is usually performed on day 2 or 3 of the period, to determine whether the conditions are ripe to begin.
During ovarian stimulation, the development of the ovarian follicles is monitored via transvaginal ultrasounds (3-4) and measurement of certain hormone levels.
Depending on the stimulation protocol followed each time, a second injection that prevents premature ovulation may be administered towards the end of the stimulation, for a few days.
When most ovarian follicles reach a diameter of 17-20 mm, a trigger shot is administered for their final maturation. The egg retrieval is scheduled for 35-36 hours later.
It is a process whereby the ovarian follicle fluid is aspirated transvaginally using a needle under ultrasound-guidance. The procedure is performed under conscious sedation and lasts around 10 minutes. The aspirated fluid is examined under microscope by embryologists to locate the eggs.
Once the egg retrieval has been concluded, you will be informed of the number of eggs collected.
After egg retrieval, you will remain in the area for 30-60 minutes or as long as deemed necessary by the medical staff, before you are ready to depart.
Pain after egg retrieval is expected to be mild and it subsides as the day goes by. It is a well-tolerated procedure, which does not usually require painkillers and women may return to work on the following day.
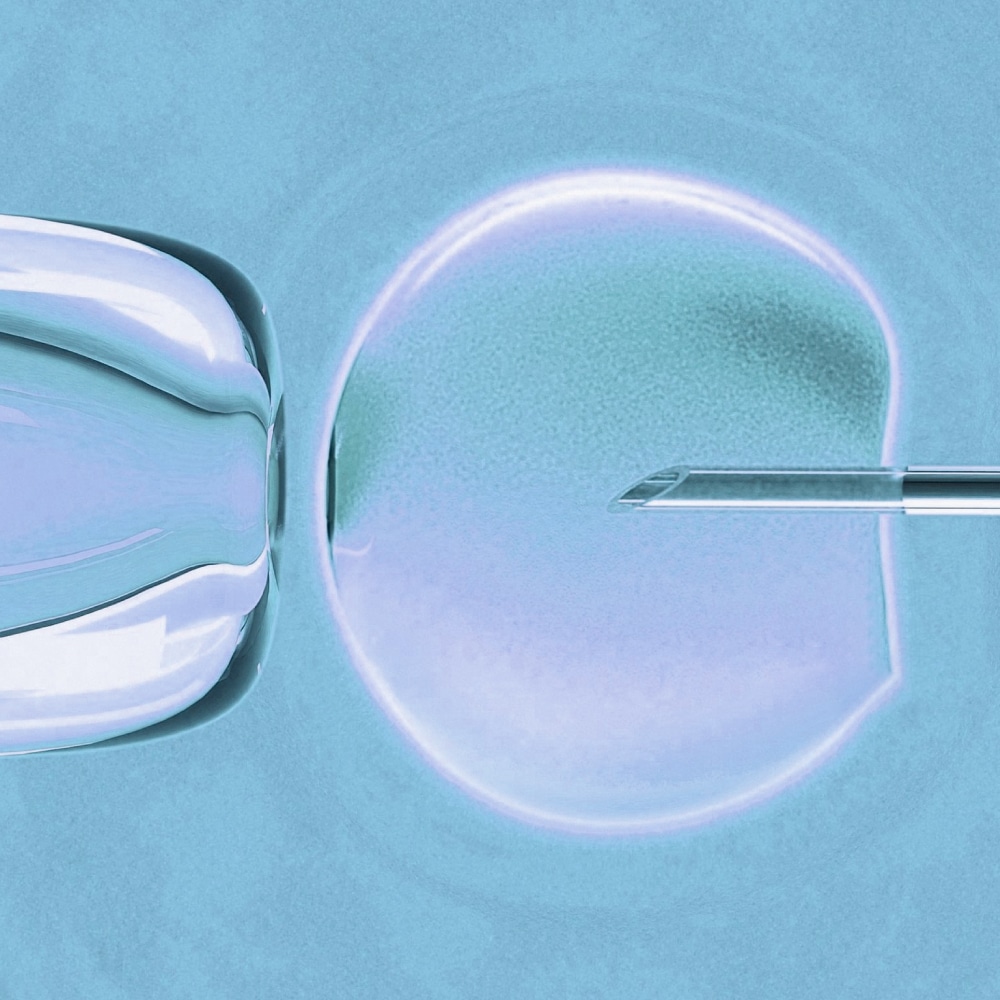
Under specific laboratory conditions, the eggs are then placed together with a quantity of sperm, so that fertilization may be achieved. Microfertilization (ICSI) may be performed if deemed necessary, such as in the case of low sperm count. On the day after egg retrieval, the couple is informed as to whether fertilization was achieved.
The fertilized eggs, i.e. the embryos, remain in incubators that mimic conditions in the womb. Some of the embryos that develop well are chosen to be transferred back to the uterus.
Embryo transfer usually takes place on the day 2 to 3 stage or on the day 5 stage (blastocyst).
The couple is informed by the embryologists or the treating physician of the quantity of embryos and the number that will be transferred to the uterus.
It is a painless procedure that is performed without anesthesia.
The embryo(s) to be transferred are aspirated with a thin, flexible catheter and then placed in the uterine cavity under ultrasound guidance.
Any embryos of satisfactory quality that were not transferred to the uterus are placed in cryopreservation for future use.
IVF Methods
The IVF method is selected after the couple has been informed of the pros and cons of each one and also depends on what the treating physician believes is the best one for the couple.
Natural-Cycle IVF
The ovarian follicle that develops in the ovary during the natural cycle is monitored via ultrasound and the collected during egg retrieval and fertilized in the lab.
No stimulation drugs are necessary. Only one injection is administered for the final maturation of the ovarian follicles, 32-36 hours before egg retrieval.
The advantages of natural-cycle IVF are that it is relatively the simplest method, no drugs are administered and it costs less (if effectiveness is not taken into consideration).
The main disadvantages are the significantly lower success rates compared to a full stimulation cycle and the higher likelihood of not having an embryo to transfer (20-30%) because of premature ovulation, or because no egg was found in the ovarian fluid, or because egg fertilization was not achieved.
It is usually recommended as a method to women with poor ovarian reserve, who, anyhow, would not produce many ovarian follicles after a possible ovarian stimulation, or to women who have shown a preference to it.
Modified Natural-Cycle IVF
It is pretty much natural-cycle IVF, meaning monitoring and egg retrieval of the single (dominant) egg produced, but with administration of drugs so as to avoid untimely premature ovulation.
Mild-Stimulation IVF
Milder or fewer stimulation drugs are administered in this case, and for a shorter period.
It is a middle-ground solution between natural-cycle and full-stimulation IVF. The success rates are very close to full-stimulation IVF.
The key benefits include the administration of lower doses of drugs, the lower cost and the lower likelihood of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome occurring.
Full-Stimulation IVF
The ovaries are stimulated after administration of gonadotropins at higher doses, aiming to produce the highest possible number of ovarian follicles.
This is the method followed in most cases, as it is the most effective.
The disadvantages for some are the administration of drugs and the higher cost. However, the cost is relative, as, according to literature, 3 or more natural-cycle IVFs are needed to come close to the effectiveness of a full-stimulation cycle.
Relevant Topics
-
Semi-Natural Cycle IVF / Mini IVF
Semi-Natural Cycle IVF / Mini IVF Mini-IVF or micro-IVF treatment is a minimum ovarian stimulation protocol during IVF. Mini-IVF...
-
Natural Cycle
Natural Cycle Natural-cycle IVF is a relatively simple procedure Natural-cycle IVF is a relatively simple procedure and consists of...
-
Ovulation Induction
Ovulation Induction It is an assisted reproduction method indicated to treat fertility problems in women who have irregular or...
-
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) The semen is treated in the lab, where active motile sperm is separated from sperm with...
-
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a process whereby the eggs are fertilized by a sperm outside of...